Macs are reliable machines that deliver in terms of software and performance.
Occasionally, your Mac may become slow or unresponsive, you may accidentally delete an important system file or some malware file could corrupt your macOS installation.
With the built-in Mac Recovery Mode feature, you can fix these and other issues you encounter on your Mac without reinstalling the macOS. You can also use Mac Recovery Mode when you want to reset a used Mac or wipe the computer clean to sell it.
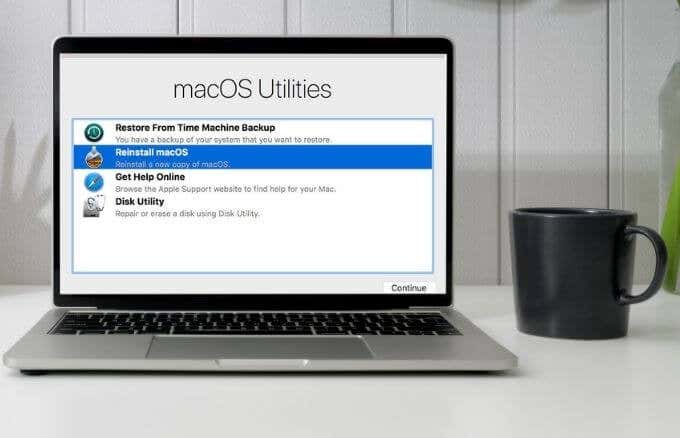
This guide explains what the Mac Recovery Mode feature does and how you can use it to diagnose or fix any issues on your Mac.
What Is Mac Recovery Mode?
Mac Recovery Mode is a built-in recovery system that lets you run emergency maintenance on your Mac. The feature loads recovery tools you can use to recover your Mac from software issues.
On a Mac with an Intel processor or with Apple silicon, you’ll find the following recovery tools:
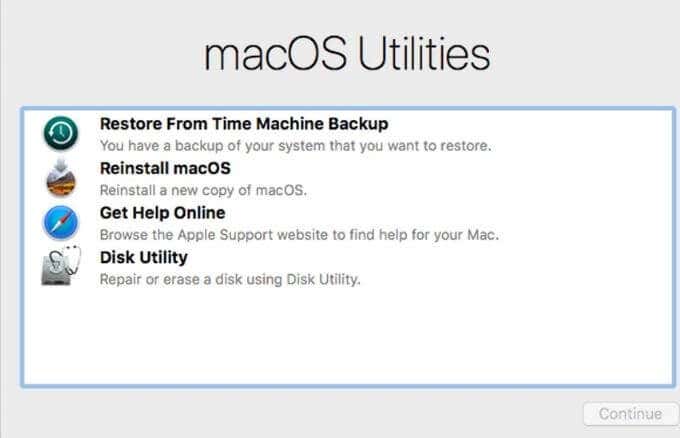
- Get help online: Lets you use Safari (with extensions disabled) to fix different issues on your Mac.
- Recovery: Provides access to more apps in Recovery Mode.
- Time Machine System Restore: Restores your data from a Time Machine backup.
- Install macOS: Reinstalls macOS on your Mac.
- Disk Utility: Repairs or erases your disk.
- Startup Security Utility: Sets the security policies for your device.
- Terminal: Changes settings through the command line.
- Share disk: Shares the disk of a Mac that’s booted in macOS Recovery mode.
- Startup disk. Sets the startup disk for your Mac.
How to Enter Recovery Mode on a Mac
Recovery Mode doesn’t delete anything on your Mac. However, if you erase a disk via Disk Utility or reinstall macOS, you’ll delete everything on your Mac.
The steps you’ll take to enter Recovery Mode on your Mac vary depending on whether your Mac shipped with an Intel processor or with Apple Silicon.
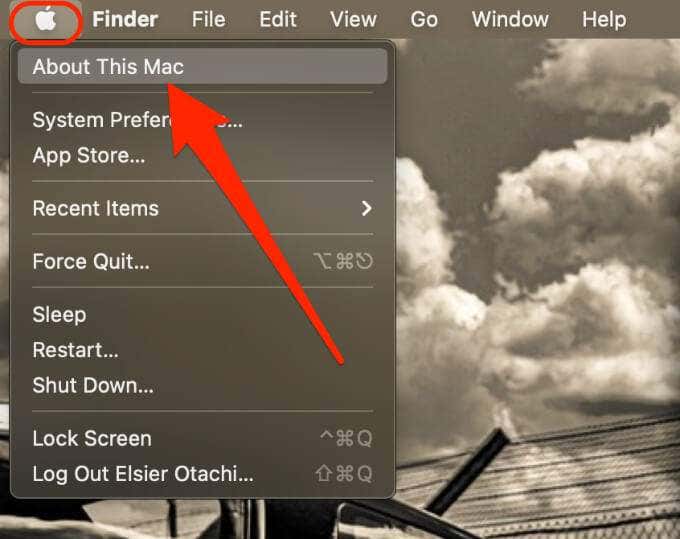
Here’s how to check the type of processor in your Mac.
- Select Apple Menu > About This Mac.
- You’ll see an item labeled Processor or Chip followed by its name. If it’s a chip, the name will read M1 Chip.
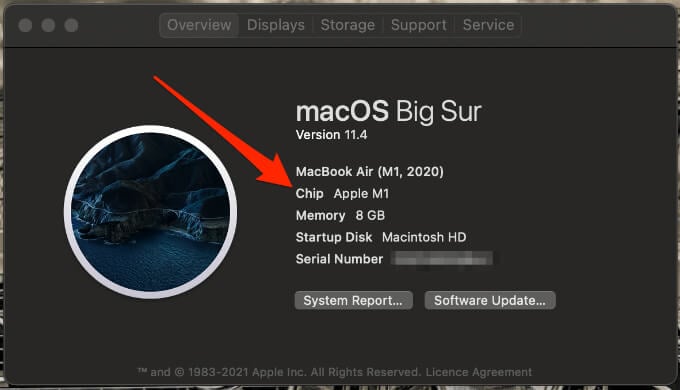
Below are the steps you’ll take to enter Recovery Mode for an Intel-based Mac or a Mac with Apple Silicon (M1 chip).
How to Start Your Mac in Recovery Mode on an Intel Mac
If you’re using a Mac with an Intel processor, use the steps below to enter Recovery Mode and resolve any issues on your computer.
- Select Apple Menu > Restart.
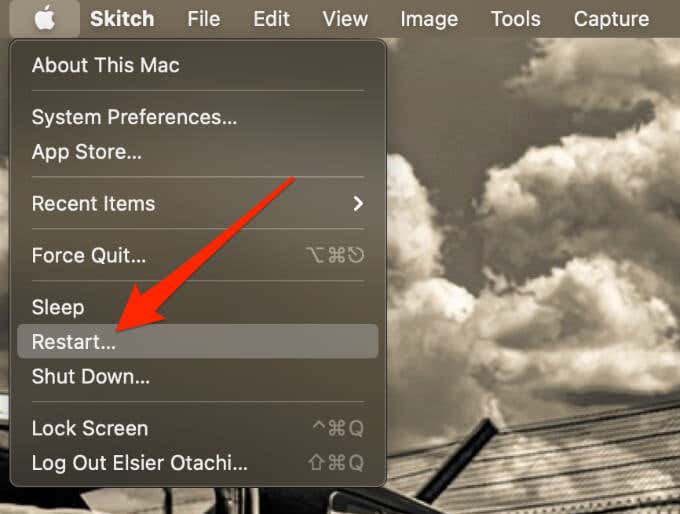
- Hold down any of the following key combinations until you see a spinning globe or the Apple logo appear on your screen.
- Command + R: Reinstalls the latest macOS version you had and lets you use other apps in macOS Recovery.
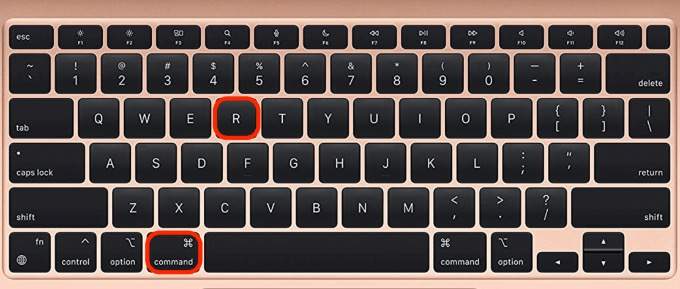
- Option + Command + R: Reinstalls macOS and upgrades it to the latest version that’s compatible with your Mac.

- Option + Shift + Command + R: Reinstalls the version of macOS that came with your Mac or the closest available.

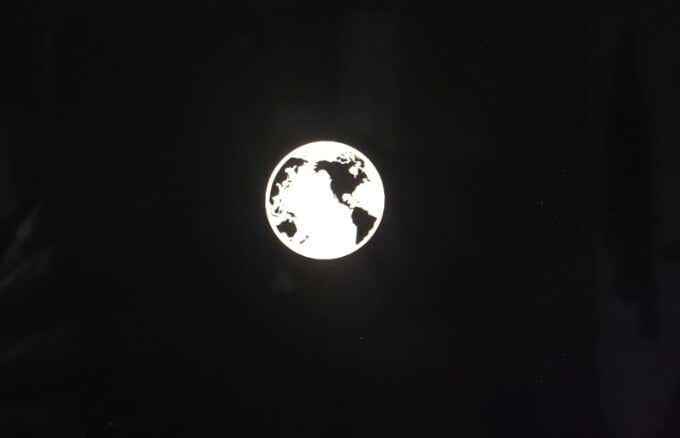
Note: If you see the spinning globe, it means your Mac is trying to boot into Recovery Mode via the internet.

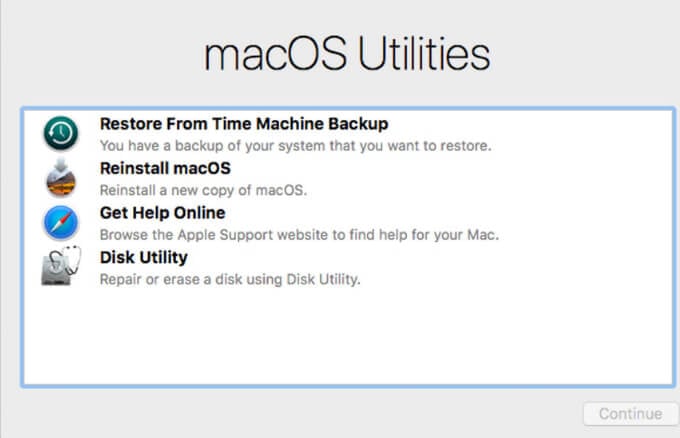
- The Recovery Mode Utilities window will open with the four recovery options: Disk Utility, Reinstall macOS, Restore from Time Machine Backup and Get help online.
How to Start Your Mac in Recovery Mode on an M1 Mac
If your Mac has the Apple Silicon chip, use these steps to enter Recovery Mode.
- Select Apple Menu > Shut Down.
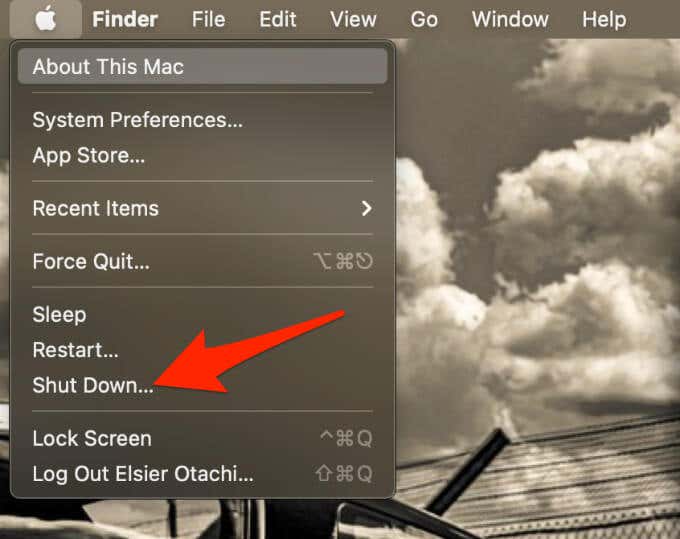
- Down press the Power button until the Loading startup options message appears on your screen.

- Select Options > Continue and then enter the admin password for your Mac.

How to Exit Recovery Mode on a Mac
Once you’re done troubleshooting or fixing issues on your Mac, select Apple Menu and then select Restart or Shut Down to exit Recovery Mode.
What to Do When Your Mac Won’t Boot into Recovery Mode
If your Mac won’t boot into Recovery Mode, here are some things you can try to resolve it:
- Shut down your Mac and try entering Recovery Mode again using the steps for the Intel-based Mac or a Mac with the M1 chip.
- Check whether your keyboard is working correctly. If not, you can try using a wired or wireless keyboard made for Mac, and ensure it’s properly plugged in.
- Reset the System Management Controller to resolve hardware issues with your Mac’s keyboard.
- Create a bootable installer for your Mac using a USB flash drive with 14 GB or more of storage. You’ll also need to download an installer for macOS Big Sur, Catalina, Mojave, or High Sierra.
- Boot your Mac into Safe Mode to repair any issues with the startup drive. Once the issues are resolved, exit Safe Mode and then try booting into Recovery Mode again.
- Use Fallback Recovery Mode. M1 Macs have a second recovery mode known as Fallback recovery OS, which you can use when the regular Recovery Mode doesn’t work. Shut down your Mac, double-press and hold down the Power button while your Mac boots up to use the feature.
- Use Internet Recovery to find a viable solution online that can help you repair your Mac. To access this feature, select the Option + Command + R key combination while restarting your Mac and follow the steps guided by the utility.
- Reinstall macOS. Make sure you have a backup of all your data and files before reinstalling the operating system.
Keep Your Mac in Good Shape
We hope you now know what Mac Recovery Mode is and how to use it to troubleshoot issues on your Mac. If you’re still having issues with your Mac, make a Genius Bar appointment or visit your nearest Apple Service Center to get one-on-one tech support.
For more on how to troubleshoot issues on your Mac, turn to our guides on how to fix Mac software update stuck installing, fix iMessage not working on Mac or fix a Mac that won’t sleep.
[related_posts_by_tax posts_per_page="5"]