Plus, what the speeds really mean
The USB-C ports on your Mac may all look the same, but they’re sometimes built differently. USB-C ports in particular have different data transfer speeds and power delivery rates. If your Mac has different USB-C ports, you may find that one port transfers data (or charges your phone) faster than the others.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to check the specifications of the USB-C ports and how to identify the fastest USB port on your Mac.

USB-C vs. Thunderbolt USB-C: What’s Different
Apple uses both the regular USB-C and Thunderbolt USB-C ports on MacBooks. As mentioned earlier, these connectivity interfaces can have varying configurations. But because they look the same, it’s often difficult to tell which USB-C port is the regular one and which uses the Thunderbolt standard.
Some laptop manufacturers differentiate these two interfaces by labeling Thunderbolt ports with a “lightning bolt” icon. Regular USB-C ports, on the other hand, usually have a USB label. Although, some manufacturers leave USB-C ports unlabeled too.

Apple doesn’t label the ports on new-generation MacBooks, so it’s almost impossible to tell USB-C ports apart by mere visual examination. In the next section, we’ll show you how to identify your Mac’s USB-C ports and their data transfer speeds.
If you’re new to the whole USB-C vs. Thunderbolt USB-C discussion, or you’d love to learn about their differences, check out this in-depth coverage of the Thunderbolt standard.
What Ports Does Your Mac Have?
When you buy a new Mac, you should see the port configurations on the spec sheet included on the packaging. Some MacBook models also have their screen sizes, year of production, and port configurations suffixed to their product name. So, when you see “MacBook Pro 13-inch (Four Thunderbolt 3 ports, 2020)”, that tells you the type and number of ports on the Mac.
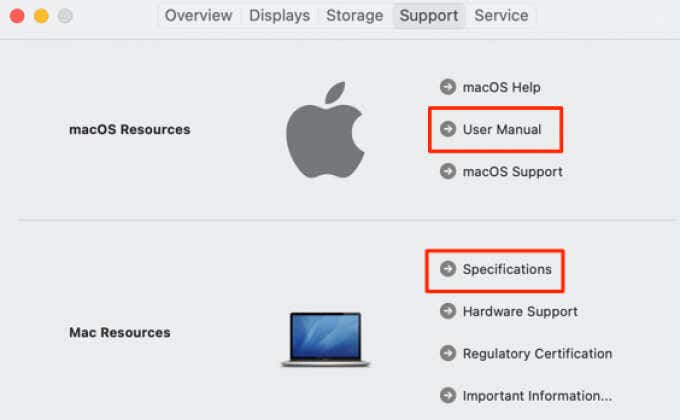
But what if you’ve disposed of your Mac’s packaging? Or, your Mac doesn’t have its port specification in its model name? Apple has a dedicated resource page that can help identify the ports on your Mac. Alternatively, check the online-based user manual or specifications for your MacBook model.
Click the Apple Logo on the menu bar and go to About This Mac > Support and select User Manual or Specifications. That’ll open a new browser window and redirect you to a web page where you can check your Mac’s port configurations.
How to Check USB-C Speed on Mac
macOS has a built-in tool that lets you check the status of your Mac’s hardware, software, and network components.
Follow the steps below to use the macOS System Information tool to check the speed of devices connected to your USB-C ports. This will give you an idea of which port is the fastest on your Mac.
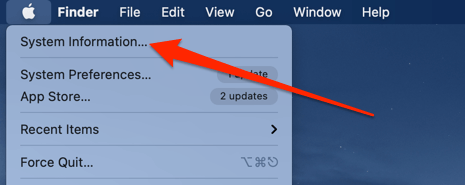
1. Hold the Option key and click the Apple logo on the menu bar.
2. Without releasing the Option key, select System Information.
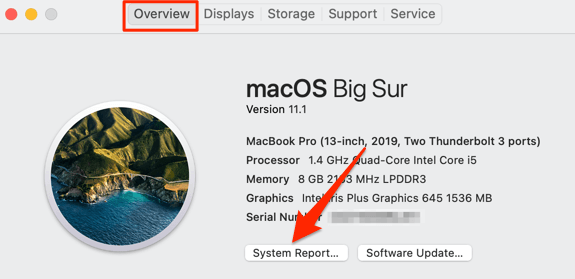
An alternate way to access the System Information tool is to click the Apple logo, select About This Mac and click System Report in the Overview tab.
3. Expand the Hardware section.

4. Scroll down the left sidebar and click on USB.
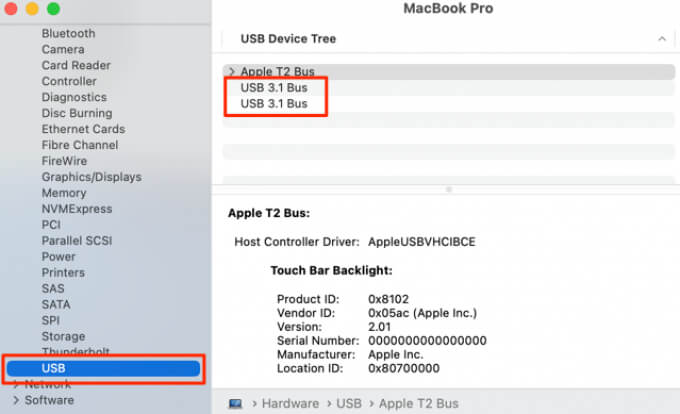
In the USB Device Tree section, you’ll find your Mac’s USB-C ports listed according to their versions. You’ll also find detailed information about the USB devices connected to your Mac.
Plug a device into any port and click the device’s name to check the speed that the device or port is capable of. Repeat the steps for other ports to check their speed.
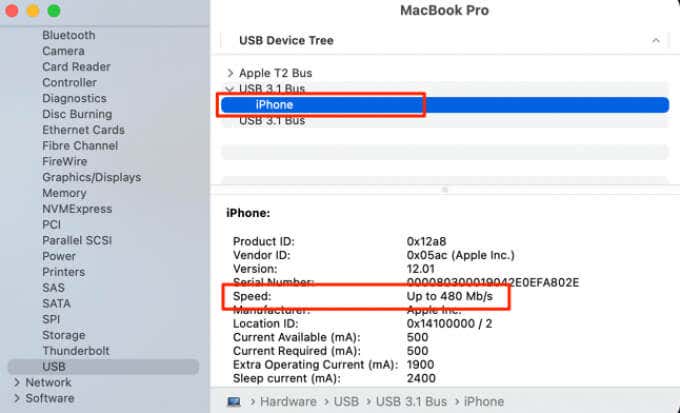
Note: If your device doesn’t appear on the USB Device Tree, close and reopen the System Information window, and check again.
If there’s a Thunderbolt option on the left sidebar, that means some (or all) ports on your Mac support the Thunderbolt standard.
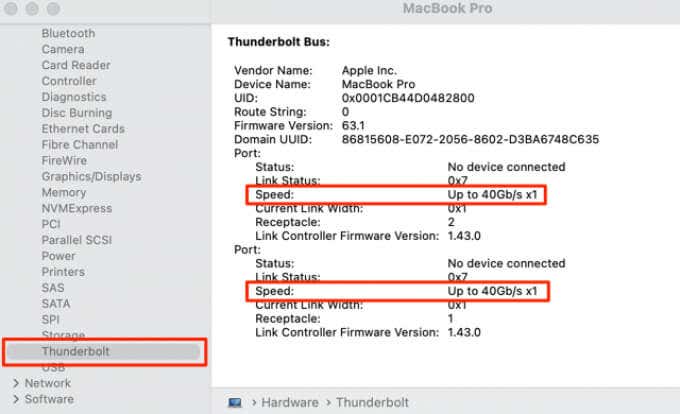
Select Thunderbolt on the left sidebar and check the Speed section for the ports and devices on the list.
USB-C Speeds and Their Meaning
The speed information on the USB Device Tree page tells you the version and specifications of your Mac’s USB-C port. These can help you find the fastest USB-C port on your Mac. Here’s what they mean:
1. Up to 1.5 Mb/sec: A USB-C port or device with this speed indicates a USB 1 connection type.
2. Up to 12 Mb/sec: Ports and devices with USB 1.1 capabilities have this speed.
3. Up to 480 Mb/sec: This tells you that the USB-C device or port is capable of USB 2.0 speeds.
4. Up to 5 Gb/s: The connected device supports USB 3.1 (Gen 1) speeds.
5. Up to 10 Gb/s: This describes the USB 3.1 (Gen 2) and USB 4 connectivity standard; they’re currently the fastest USB-C ports on any Mac.

For optimal transmission speeds, your USB device(s) and USB-C cable must also support the same USB standard as the port. So, to enjoy USB 4 speed (up to 10GB/s), your Mac, the USB-C device, and USB-C cable must all support the USB 4 standard. Take note of this when buying USB-C accessories and peripherals. Also, refer to our explainer on USB cable types to learn more.
A USB-C hub (or adapter) can also slow down the potential data transfer speed between your Mac and USB-C devices. Make sure the adapter or USB hub supports your Mac’s USB-C standard. Otherwise, connected devices will be limited to the speed of the USB adapter.

For context, if you plug a USB 2.0 hub into your Mac, devices connected to the hub will be limited to USB 2.0 speed. For the best experience, plug devices directly into your Mac or use compatible accessories.
USB-C: Thunderbolt 3 Vs Thunderbolt 4 on Mac
MacBooks come with Thunderbolt, Thunderbolt 2, Thunderbolt 3, and Thunderbolt 4 ports. However, only the Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 standard use the USB-C interface. They are backward-compatible high-speed ports that work with all USB-C specifications/generations. Both standards also have the same 40Gbps maximum data transfer speed, but Thunderbolt 4 is superior.
Thunderbolt 4 comes with better security and improved support for video data transfer. For context, a Thunderbolt 4 USB-C connector can transmit video signals to one 8K display or two 4K displays. Thunderbolt 3, on the other hand, can only handle one 4K display. Currently, only the latest M1-powered Macs introduced in 2020 ship with Thunderbolt 4 or USB-4 ports. Future releases will most definitely use the Thunderbolt 4 standard, too.
Still don’t grasp the whole concept of USB-C and Thunderbolt connectivity? Or perhaps, you have some unanswered questions? Leave a comment below and we’ll try to get you some answers.